We all know that smoking has a lot of deleterious effects on multiple organ of the body and causes cardiac disease, lung problems, reproductive disorders and various cancers. But what is little known is that smoking affects the bones as well as the discs in the spine. Lot of population based studies have demonstrated that smokers are more likely to develop spinal pain than non-smokers.
Osteoporosis or porous and fragile bones is a very common ailment in women after menopause and to a lesser extent in men over 65 to 70 years. Various studies have shown that smoking increases the loss of bone mass and leads to increased risk of fractures in both men and women.

Ward K.D and Klesges R.C of The University of Memphis Center for Community Health, conducted an analysis of the effects of cigarette smoking on bone mineral density. (Calcif Tissue Int. 2001 May ; 68(5): 259–270.). They found that smoking has an independent and dose dependent influence on bone loss and increased risk of fractures.
Based on their data, it is estimated that smoking increases the lifetime risk of developing a vertebral fracture by 13% in women and 32% in men. At the hip, smoking is estimated to increase lifetime fracture risk by 31% in women and 40% in men. They also concluded that stopping the smoking can stop or may even reverse the bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
Another study (Eur J Radiol. 2017 Apr;89:177-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.011.) concluded that current smokers have a more rapid decline in the bone mineral density over a three year period compared to former smokers.
The discs in the spine are also at a higher risk of developing accelerated wear and tear changes due to smoking. (Elmasry S, Asfour S, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Travascio F. Effects of Tobacco Smoking on the Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disc: A Finite Element Study. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136137. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136137).
It is not uncommon to see multiple level lumbar and cervical disc degeneration and related problems in chronic smokers. The discs are located in between two vertebral bones. The discs do not have direct blood supply and depend on diffusion of nutrients and oxygen from the blood vessels in the adjacent bone.
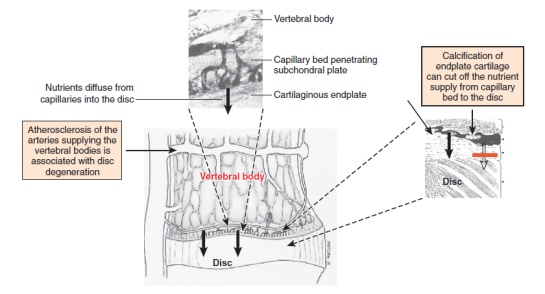
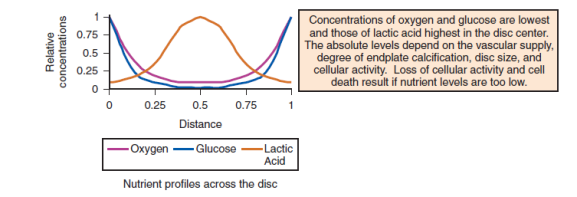
Smoking reduces the blood flow in the small blood vessels in the vertebral bodies thereby impairing the diffusion of nutrients and oxygen into the adjacent discs and accumulation of waste material inside the disc matrix, both factors leading to faster degeneration of the discs.
Nicotine has a detrimental effect on the cartilage cells in the disc which are responsible to maintain the matrix of the disc. It induces cell death and enhances activity of enzymes that cause degradation of the extra-cellular matrix of the disc substance thereby accelerating the wear and tear changes.
It is also established that if smokers need a spine surgery, they are likely to have a higher rate of complications like non-union (lack of bone formation at operated levels) or wound infections compared to non-smokers.
So, this information adds another very important reason to the list of reasons why one should quit smoking!.
Quitting smoking is hard. The National Cancer Institute (USA) recommends these five steps be the START of every successful plan to quit smoking.
• Set a quit date.
• Tell family, friends and co-workers you plan to quit.
• Anticipate and plan for the challenges you will face while quitting.
• Remove cigarettes and other tobacco products from your home, car, and workplace.
• Talk to your doctor about getting help to quit.
If you liked the article, please share it and subscribe to my future articles on spine problems. Thank you.!

With years of experience in spine surgery, Dr Phani Kiran S, Senior Consultant Spine Surgeon will assess you and suggest the treatment option that is right for you.
We at Medspine clinics, understand the importance of educating all our patients about the spinal problems and the most effective ways to take care of their spine.
The Ortho Clinic: Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Saturday.
Ojas Health: Tuesday, Thursday
© Copyright 2024 MedSpine. All Rights Reserved. Build with 🤍 by Digital GYB
WhatsApp us